Robotics, an interdisciplinary branch intertwining engineering, computer science, and on occasions, biology, treads on the path to conceive, construct, and utilise robots. These programmable machines can manifest in a myriad of forms, each tailored to a unique purpose. From humanoid robots capable of mimicking human actions and responses to specialised industrial robots executing precise operations, robotics continues to expand its breadth and depth.
Let us look into some of the key components that facilitate the functioning of these marvels of engineering:
Actuators.
The lifeline of robotic motion, these elements morph energy into movement, propelling robots and equipping them with interactive capabilities.
The field of robotics has witnessed a multitude of advancements and found its niche in a wide array of applications, summarised below.
Industrial Robotics.
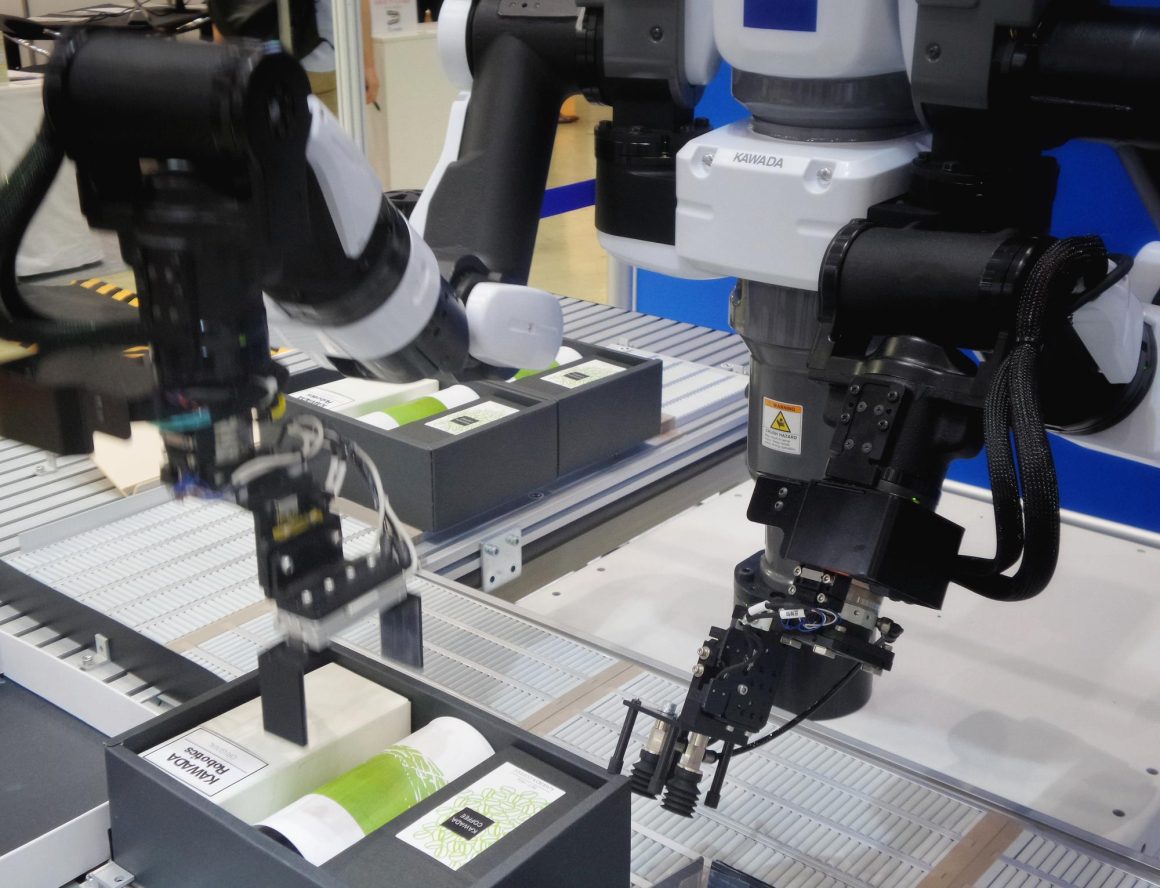

Industrial robots have become increasingly proficient, performing a wide range of tasks from assembling and painting to welding, packaging, and inspecting products. Their movements have grown precise, and they have been designed to safely collaborate with humans.
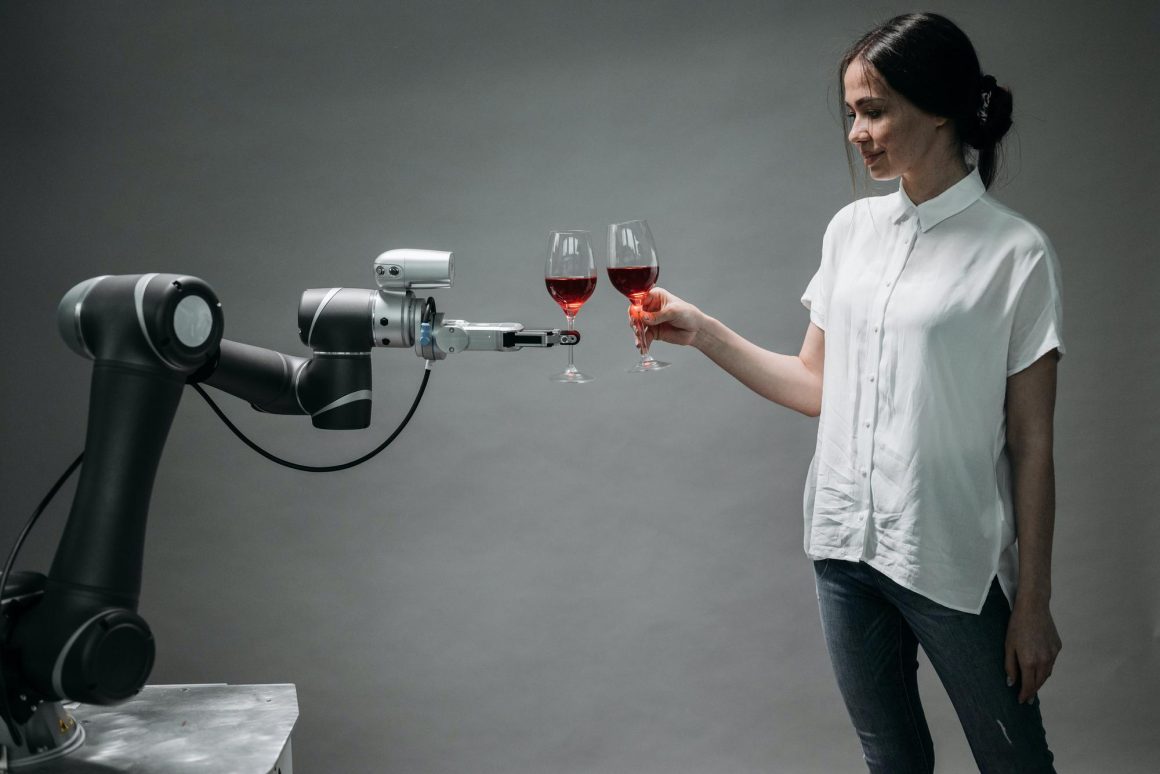
Service Robotics.

These robotic helpers have become more common in various settings like homes, hospitals, and public spaces, assisting with tasks such as cleaning, cooking, and personal care.
Medical Robotics.
Robots have stepped into the medical field, carrying out surgeries, aiding in rehabilitation, and delivering drugs. Some surgical robots have even outperformed humans in terms of procedural precision.
Autonomous Vehicles.
These robotic entities, capable of moving around and accomplishing tasks without human intervention, span drones, self-driving cars, and underwater exploration robots.
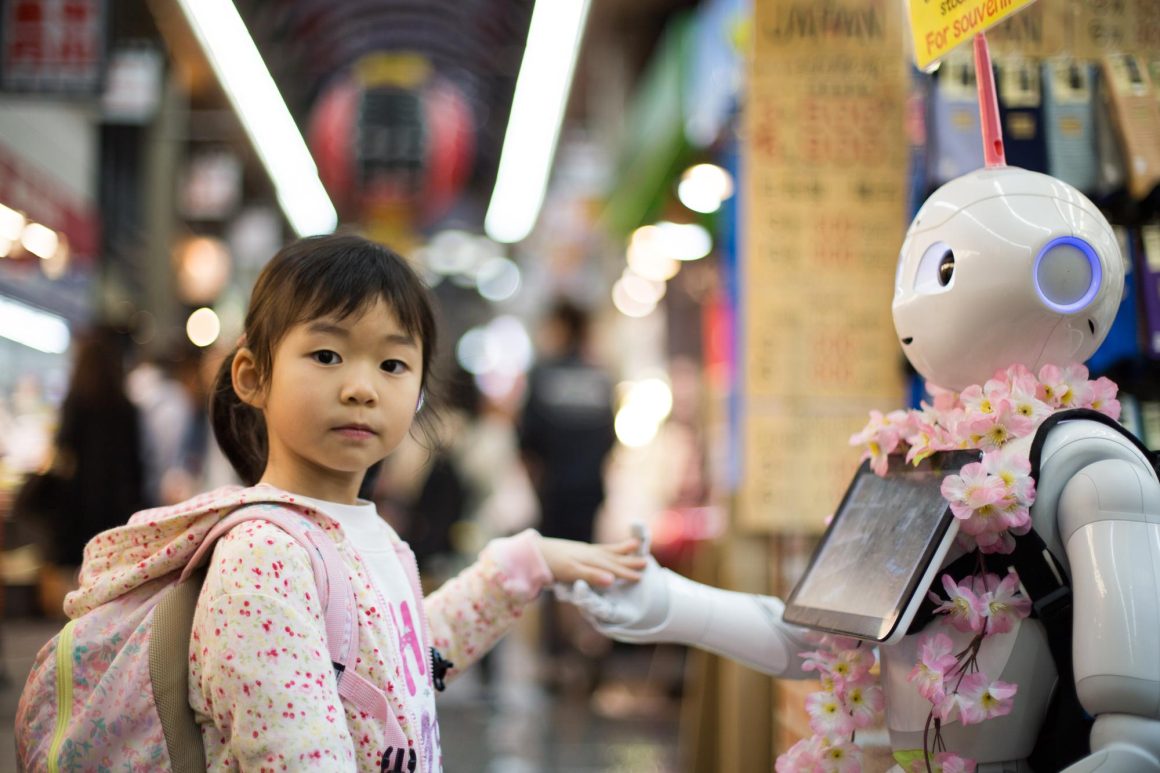
Social Robotics.

As social companions, these robots interact with humans on an emotional level, and have found their place in education, therapy, and entertainment sectors.
Research Robotics.
Robots have been invaluable in research settings, serving to test algorithms, study human-robot interaction, or even model biological systems.
However, the world of robotics is not devoid of challenges. Issues related to autonomy, safety, energy efficiency, and robustness of robots in unstructured environments often surface, pointing towards the active areas of research in the field.
Robotics, in its essence, represents the epitome of technological progress, continually pushing the boundaries of what machines can do, and profoundly shaping our world and future. In the coming years, we can expect robotics to further permeate our lives, transforming industries and redefining human-machine interaction.